The Brain of your Car: ECU Explained
Engine Repair
By Sanumotors Research Team
Sat May 03 2025
SHARE THIS ARTICLE
466 views
5 minutes read
The Brain of your Car: ECU Explained
Have you ever noticed a warning light flashing and wondered what’s really going under the hood?
Older vehicles relied entirely on mechanical systems. But today’s cars are basically computers on wheels. The brain of these cars is called Electronic Control Unit (ECU), which monitors and control various functions of the car.
It will take information from various sensors and eventually make adjustments to deliver better performance, safety and comfort.
ECUs consist of a microprocessor, memory, input/output interfaces, and software that controls the system’s function.
There are various control modules which are part of vehicle ECU Network. ECU communicate with other control modules within the vehicle ensuring that different vehicle systems work together harmoniously.
Some common modules are listed below.
ECM (Engine Control Module)
Commonly known as Engine Control Unit. This module is responsible for optimizing engine performance. It controls fuel injection, air-fuel mixture, ignition timing and exhaust gas circulation to optimise engine performance and fuel efficiency.
TCU (Transmission Control Unit)
This module ensures smooth transmission of gears. It monitors engine load, speed and throttle position to determine the optimal time to shift gears.
Brake Control Module
This module handles the vehicle braking system particularly Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) and Traction Control
BCM (Body Control Module) / CCM (Comfort Control Module)
This module controls the stuff inside the vehicle such as windows, door locks alarm etc.
FCM (Fuel Control Module)
Usually, this module is integrated within the ECM but sometimes it is given as a separate module depending on the complexity of the vehicle’s ECU Network. It controls how fuel should be used.
Airbag Control Module
The airbag ECU monitors sensor data from around the vehicle to determine whether a collision is severe enough to deploy airbags. It’s a critical safety component that ensures the protection of passengers in the event of a crash.
Battery Management System Module
In electric and hybrid vehicles, the Battery Management System (BMS) oversees the battery's condition, monitoring aspects like charging and discharging cycles, temperature, and voltage to ensure the battery's safety and longevity.
ADAS Control Module
The latest cars are equipped with advanced driver-assistance systems like adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assistance, automatic parking, and collision avoidance. These ECUs handle complex algorithms and rely on a range of sensors such as cameras, radar, and LiDAR to enable these systems
If something is wrong with a component the associated module will send a code and then a warning light will blink in the dashboard. This makes the diagnostics easier.
How does ECU work?
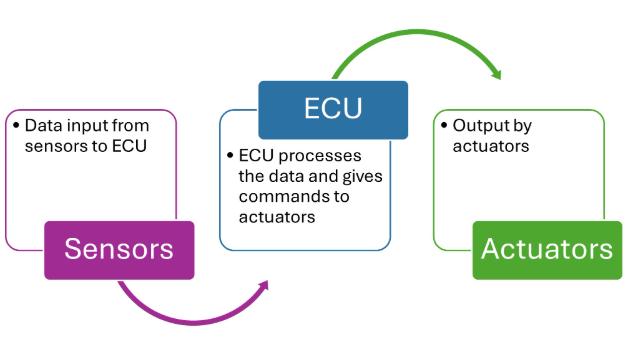
There are various sensors around the car. These sensors continuously monitor various parameters (engine temperature, speed, fuel pressure, tire pressure, brake system status etc.) and send real time data to Electronic Control Unit.
The ECU acts as the brain of the vehicle. It processes the data and makes decisions based on preprogrammed algorithms and real time conditions. Then ECU sends commands to actuators (fuel injectors, brakes, transmission etc.) to adjust the vehicle’s system.
ECU operate based on feedback loop. Once the actuators made the necessary adjustments, they send feedback to ECU, indicating whether the commands were successful or need further adjustments. This feedback loop ensures the vehicle continuously operate efficiently
For example, if a wheel locks up during braking, the ABS ECU monitors wheel speed sensors and adjusts brake pressure to prevent skidding.
If the engine control unit detects a drop in engine performance or a sensor send a high temperature measurement to ECU, it will adjust the fuel mixture and ignition timing to optimise engine performance.
Signs you might need ECU Repair
Check Engine Light comes on
Poor Engine Performance
Transmission Problems
Electrical System Malfunction
Increased Fuel Consumption
ECU Repair

Diagnostic tools are used to scan the vehicle’s onboard computer system for error codes. This helps determine whether the problem lies with the ECU or another part of the vehicle.
Once a faulty ECU is identified, it needs to be carefully detached from the vehicle, as the ECU is often placed in hard-to-reach spots, and connectors must be disconnected properly to prevent any damage.
Then the ECU is inspected to determine whether it needs a repair or replacement. Minor issues may be repaired, while severe damage may require a full replacement.
New or repaired ECUs often need to be reprogrammed to sync with the vehicle. After repairs, the ECU is tested to ensure proper communication with sensors and actuators.
Role of ECU in modern vehicles,
Improved Performance
Enhanced Safety
Increased Comfort
Autonomous Driving
Real-time Diagnostics
In future, we can expect ECUs to become even more sophisticated, interconnected, and crucial for the operation of our vehicles. It’s clear: the future of automotive design is deeply intertwined with the evolution of ECUs.
SHARE THIS ARTICLE
466 views
5 minutes read
Comments
Loading...
Loading...
